Resilient Power Infrastructure and System under Extreme Weather
|
|
|
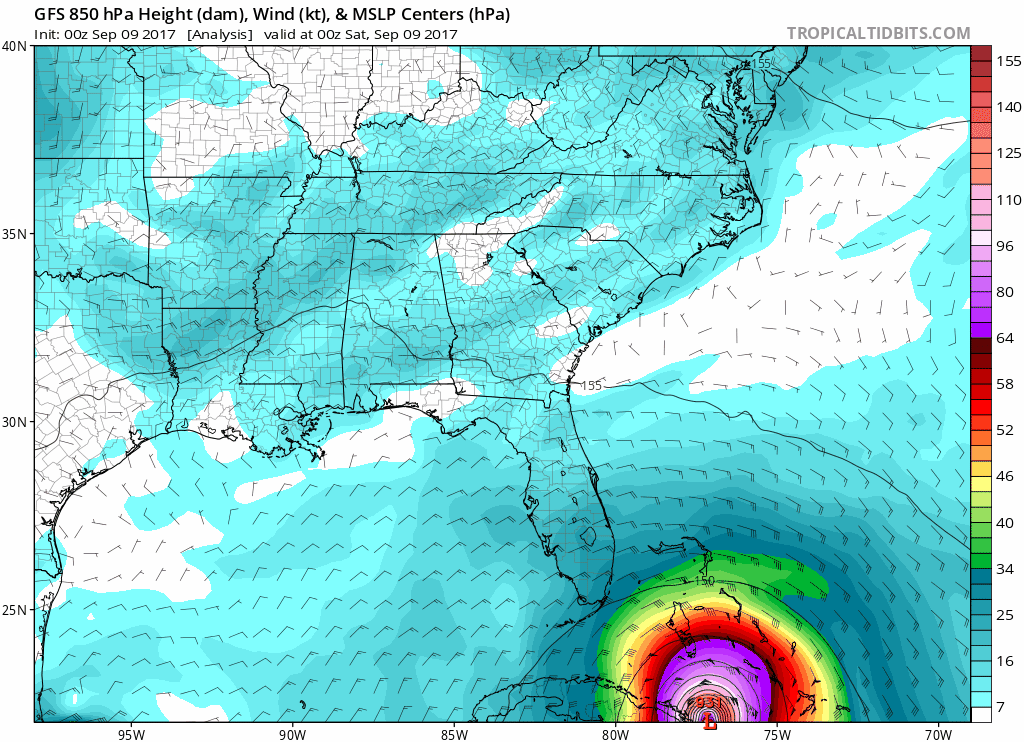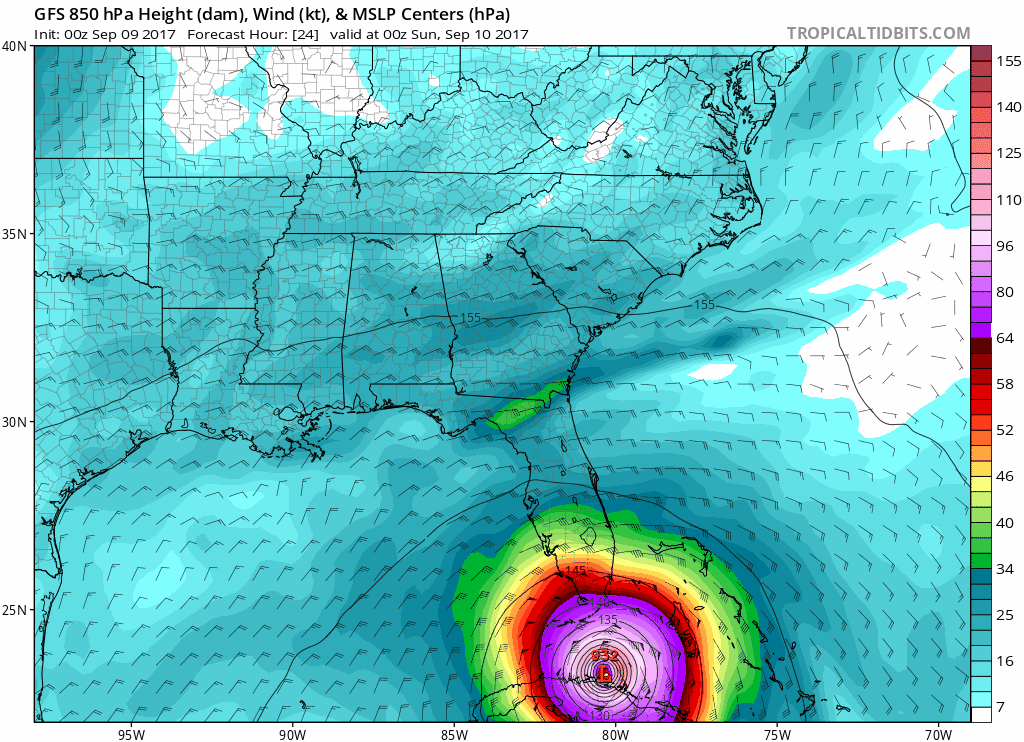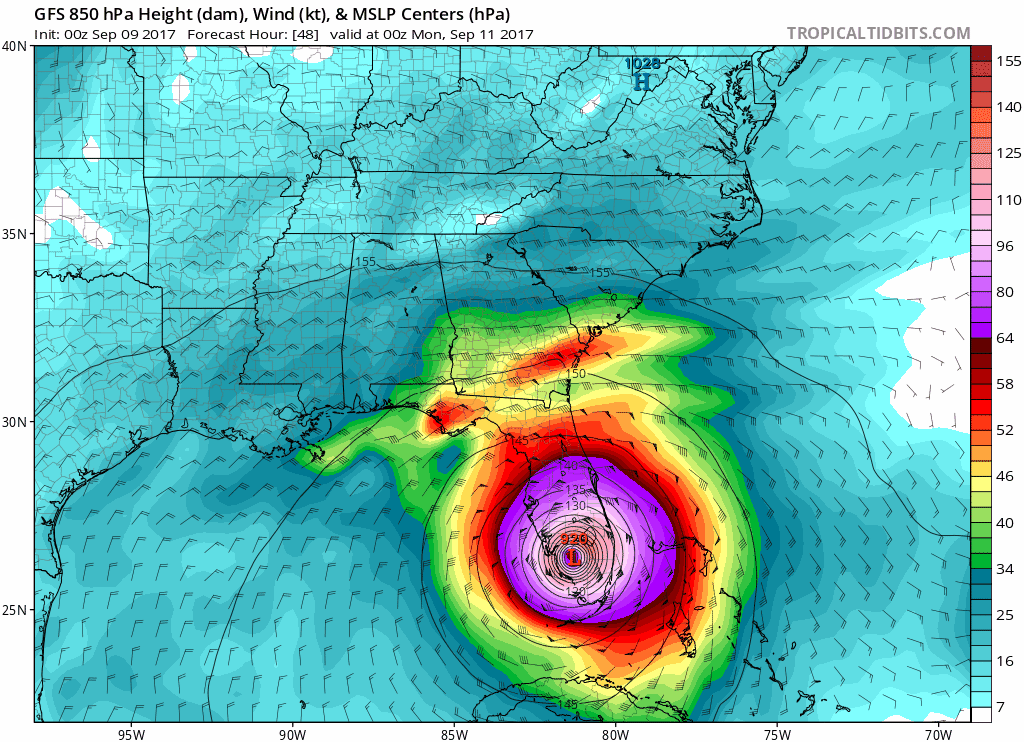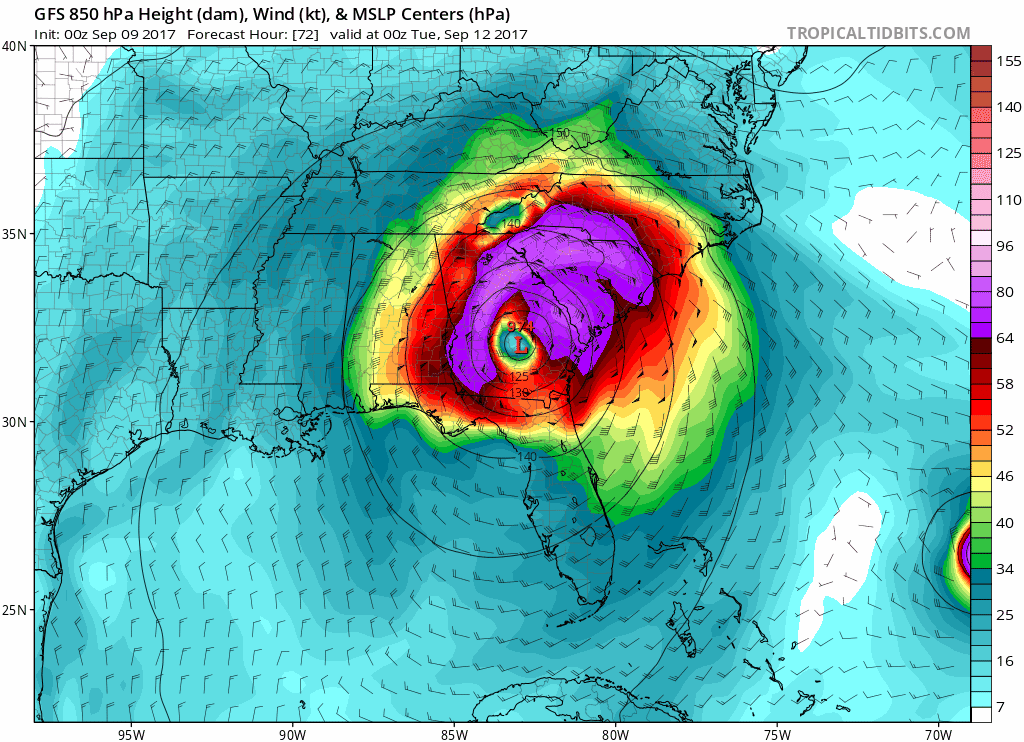
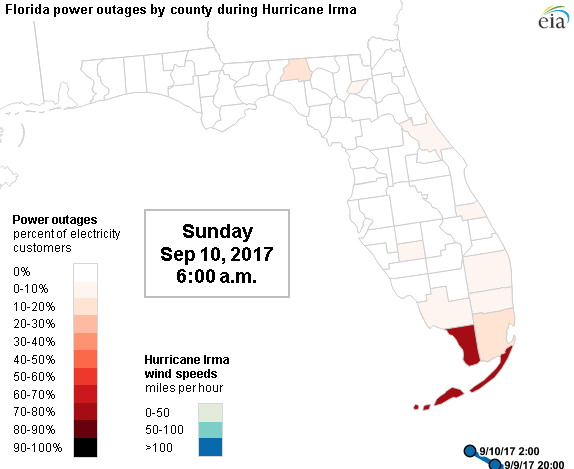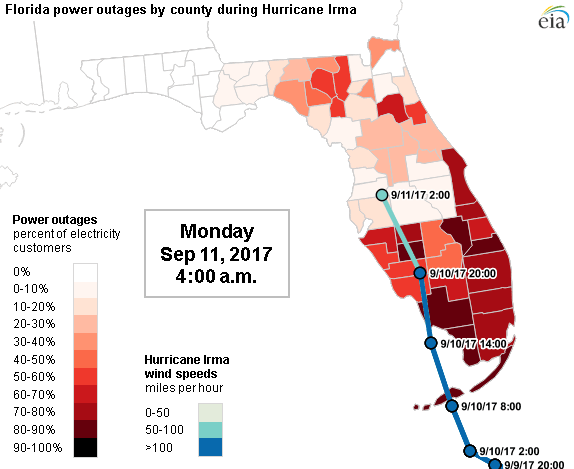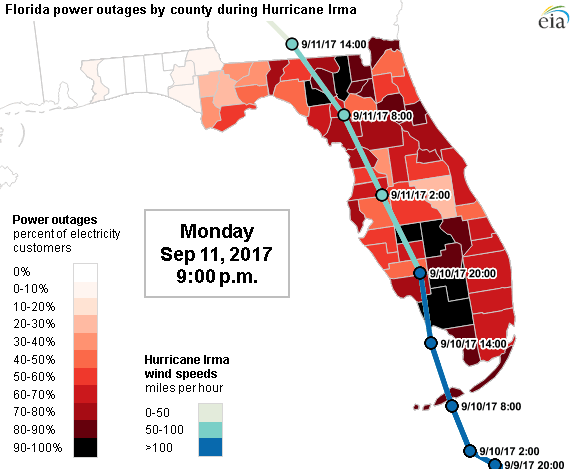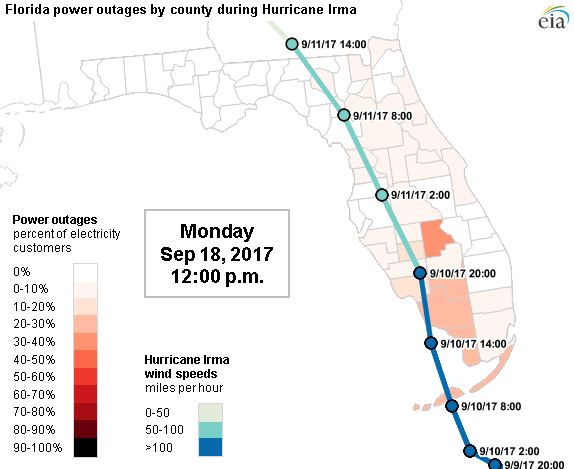
| Hurricane wind field progressing and Power Network Outage during 2017 Irma Hurricane | |
This work continues the multidisciplinary initiative WeatherG, which aims to understand the physical-law-based chain effect of the increasingly frequent extreme weather events on the power systems and mitigate their impact on the power networks.
See more about the initiative here.
Related Research project:
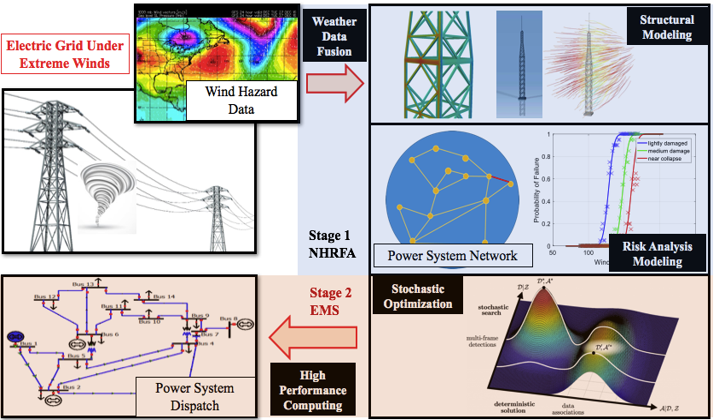
The Weather Resilient Electric Grid Operation Cyber-System to be developed will revolutionize power system operations under extreme weather, thereby unleashing unprecedented levels of reliability and economic efficiency. Two modules are integrated into the system:
- Natural Hazard Related Failure Analysis (NHRFA) module will predict the vulnerability of transmission lines with weather data infusion in the GIS.
- The Energy Management System (EMS) module will analyze the vulnerability of the system to regular and hazard-induced outages. Then, it will optimize/control the dispatch of the generators to (a) minimize the cost and (b) ensure reliability.
Research Spotlight: OUR First Work HERE
EAGER: Real-Time: Effective Power System Operation during Hurricanes using Historical and Real-Time Data
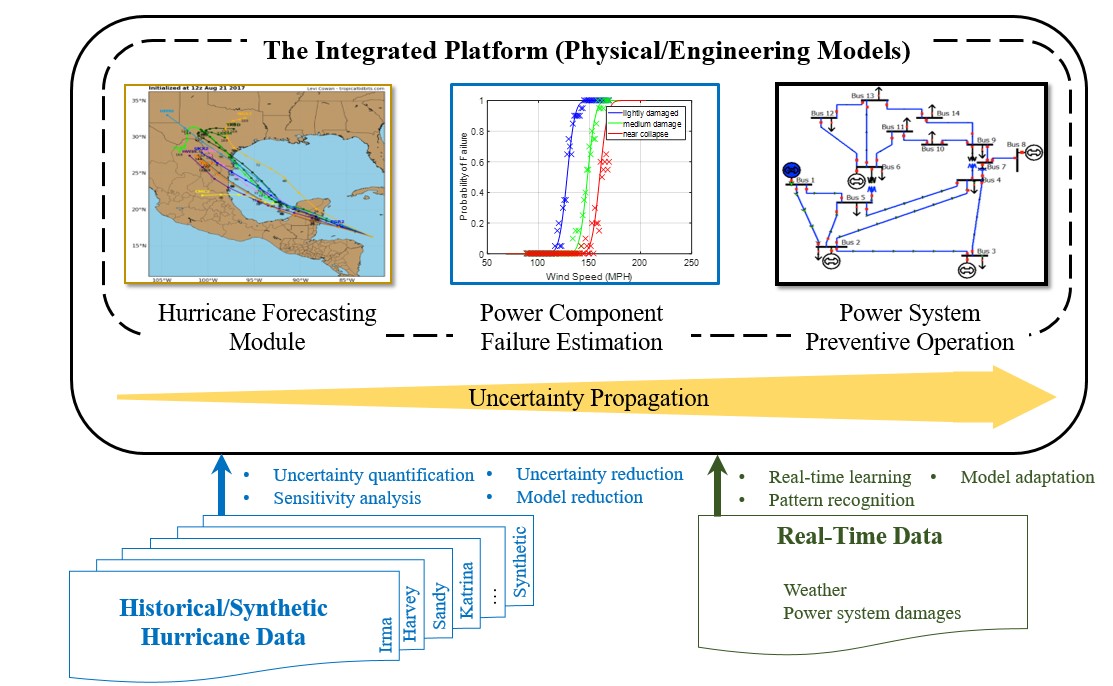
This project exploits the availability of weather forecast data to guide preventive power system operation during hurricanes. Currently, weather forecast data is not systematically integrated into the power system operation and, thus, the preventive operation is not possible. The current research approaches employ an integrated framework, mainly based on physical and engineering models, which uses hurricane forecast information to predict the component damage scenarios for the power system. The preventive operation decisions are, then, determined with stochastic optimization, through explicit modeling of the damage scenarios.
Research Spotlight: HERE
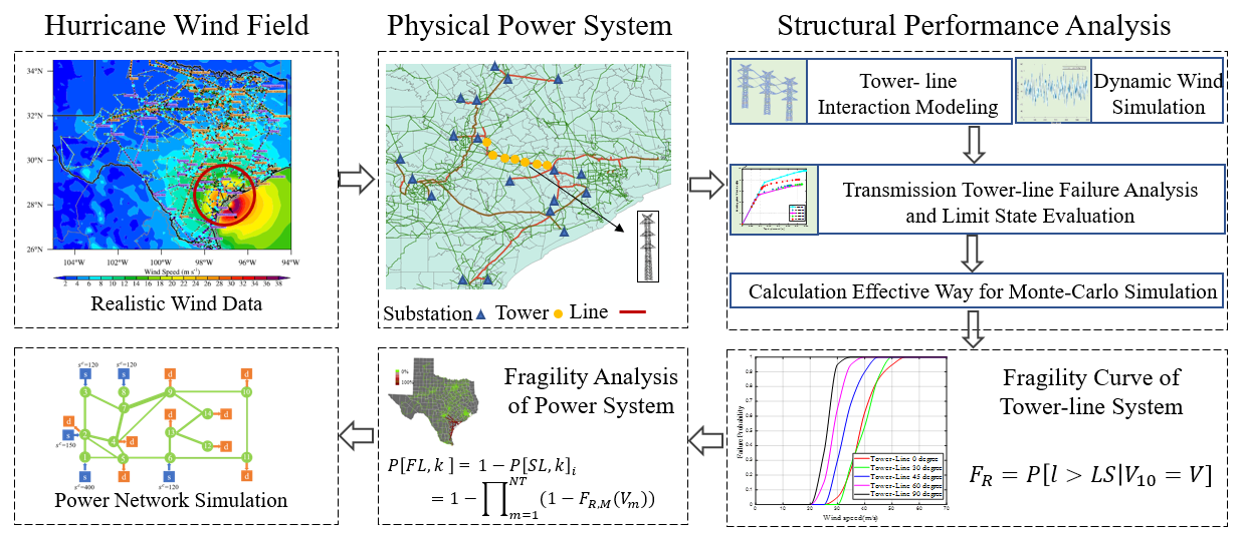
This project addresses that gap in knowledge in dealing with high wind disaster events for preventative and restorative resiliency of electric power networks. By integrating multiple data sources into a robust simulation tool, researchers can design new methods to mitigate the impact of hurricanes and other extreme wind events on power system operations. The outcomes of the research would positively impact reliability, resiliency, and delivery of electric power to US population centers.
Research Spotlight: Here
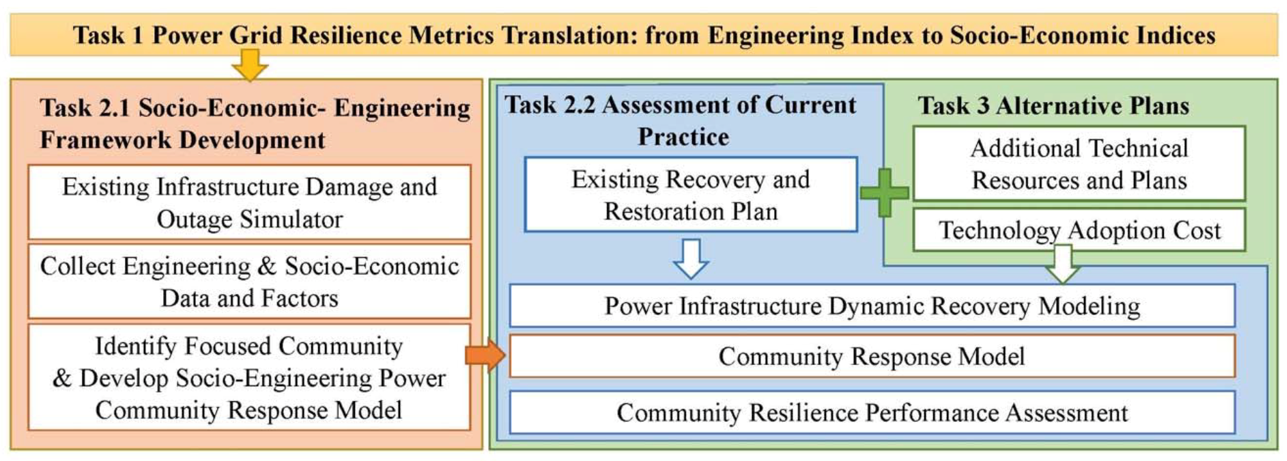
This study looks at the failure of the electric grid, aiming to improve understanding of how the electric grid can be designed to ensure that the most vulnerable people in the U.S. are not also the most likely to experience and be harmed by grid failure. Severe weather is the leading cause of power outages in the United States. Outages created by grid failure, when the electric grid fails to provide reliable service, can cause serious adverse impacts ranging from economic damage to possible loss of life. Grid failure and the impacts of grid failure are not distributed equally across all geographies and social settings, meaning that outages are more likely to occur in places where the grid is not prepared to respond to grid failure and the impacts of grid failure are more likely to harm already vulnerable communities and groups. This project provides new knowledge for strengthening American critical infrastructure, including the electrical grid infrastructure as well as other built infrastructures and social infrastructures that shape the vulnerabilities involved in disaster response management.